Sustainability Impact Assessment
The assessment of materiality is a crucial policy for Chunghwa Post when it comes to the compilation of sustainability reports, formulation of long-term sustainability goals, and guidelines for communication with the stakeholders. In accordance with the GRI Universal Standards 2021, the methodology of materiality assessment incorporated economic, environmental and social aspects, along with the actual and potential positive or negative impacts. Meetings were also convened for consultations with internal and external experts for the determination of the prioritization of the material sustainability topics and their boundaries for the 2024 Sustainability Report.
Step 1: Identify targets for communication
Conducted stakeholder identification and engagement in accordance with GRI standards of Stakeholder Engagement and identified 8 categories of stakeholders.
Step 2: Collect sustainability-related topics
Understand or collect stakeholders’ views and opinions on internal and external issues of concern through the Sustainable Development Committee.
Step 3: Identify actual and potential impacts and assess their significance
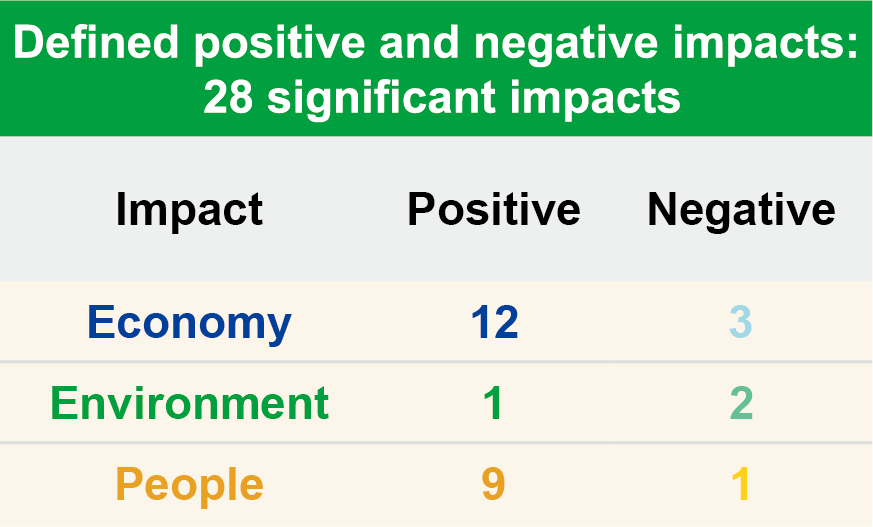
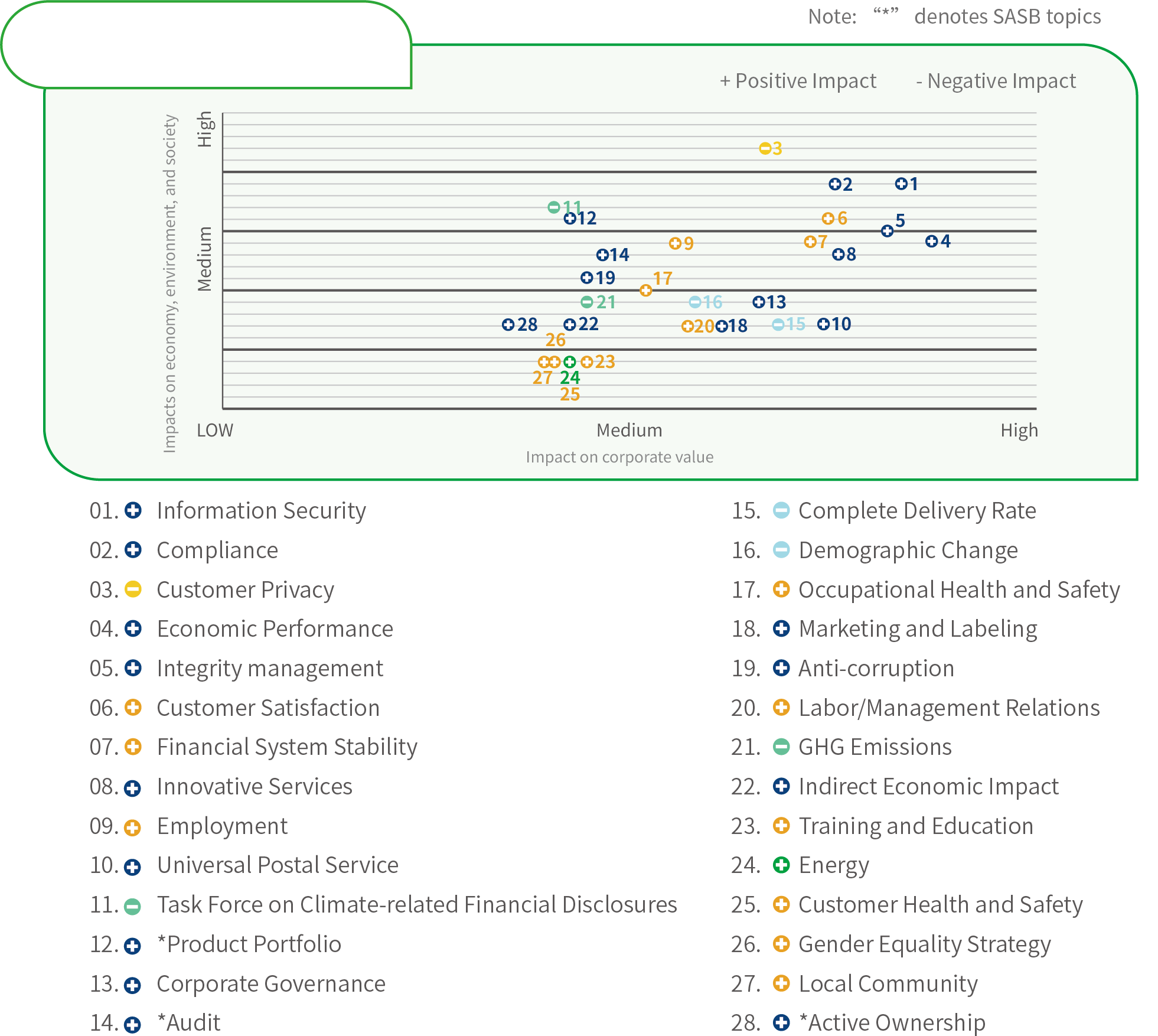
Evaluated the level of significance of the impact of the topics and ranked these topics based on their results of positive and negative impacts. This year, a total of 28 material sustainability topics were identified, including 22 with positive impacts and 6 with negative impacts.
Chunghwa Post further evaluated the impact of the material topics on organizational operations and conducted double materiality analysis. Chunghwa Post Sustainable Development Committee and relevant high-level executives scored the impact of the material topics mentioned above. The results of level of impacts of “environment, economy, people (including human rights) were integrated, a double materiality matrix was produced.
Chunghwa Post further evaluated the impact of the material topics on organizational operations and conducted double materiality analysis. Chunghwa Post Sustainable Development Committee and relevant high-level executives scored the impact of the material topics mentioned above. The results of level of impacts of “environment, economy, people (including human rights) were integrated, a double materiality matrix was produced.